Beyond Breakdowns: The Strategic Value of Preventative & Predictive Maintenance in a Facility
In today’s fast-paced world, where every moment counts, the stakes for facility management have never been higher. Imagine a bustling office, a state-of-the-art manufacturing plant, or a critical healthcare facility—all operating seamlessly, powered by the strategic foresight of preventative and predictive maintenance. This proactive approach not only shields organizations from unexpected breakdowns but also transforms maintenance from a daunting yet necessary task into a powerful asset. By harnessing innovative technology, facility managers can implement regular inspections and timely repairs that keep operations running smoothly.
It’s about creating a culture of reliability, optimizing asset longevity, and ensuring that every piece of equipment contributes to a flawless workflow. Let’s dive deeper into how this strategic approach can redefine maintenance in facilities to elevate performance.
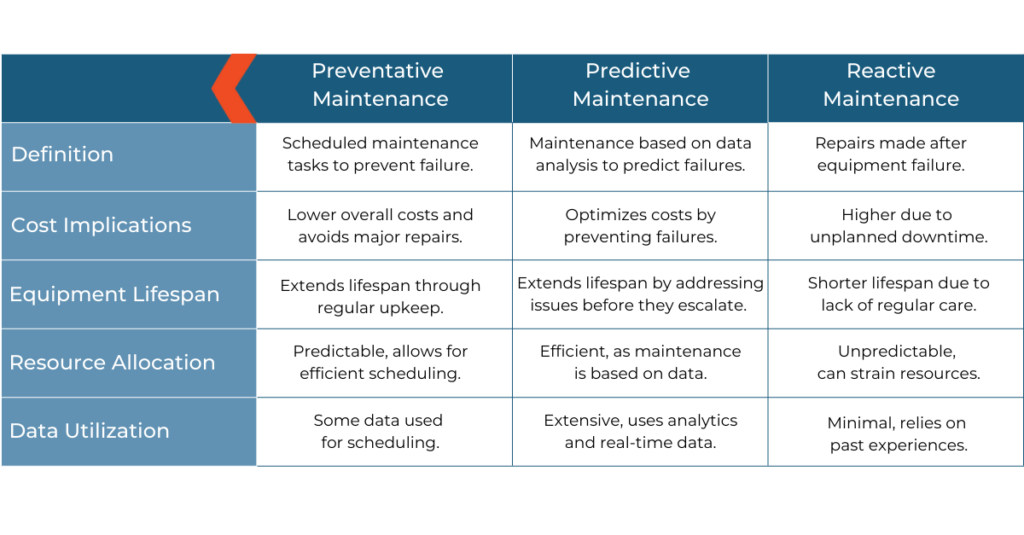
What is Preventative and Predictive Maintenance?
Preventative maintenance is a proactive approach to management aimed at preventing equipment failure and reducing the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns, involving regularly scheduled inspections, repairs, and upkeep tasks before issues arise. Predictive maintenance is an advanced strategy that utilizes data analytics and machine learning to predict equipment failure.
Contrarily, reactive maintenance, also known as “run-to-failure” maintenance, is a strategy where repairs are made only after equipment or machinery has already failed.
Why is it Important?
The foundation of a smooth-running facility is prevention, while using tools to help predict issues that may arise. Rather than waiting for equipment malfunction to occur, organizations should consider how to maintain long-term asset productivity with the combination of preventative and predictive maintenance practices. It has proven benefits in reducing downtime, improving equipment reliability, and optimizing operational efficiency. This approach can extend the lifetime of assets, reduce downtime, maintenance costs and avoid long-term expenses and disruptions.
According to a survey, only 51% of technician hours are spent on preventative maintenance tasks which they perceive as too low. This leaves organizations room to upscale their operations to avoid future disruptions.


Preventative and Predictive Maintenance is Driven by Technology
Technology plays a pivotal role in reshaping conventional preventative and predictive maintenance practices. Various technological advancements are driving a significant transformation in how organizations approach maintenance tasks and asset management such as:
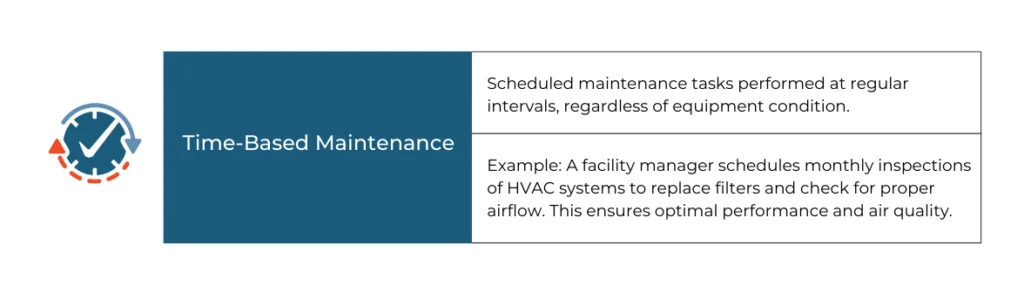
| IoT Sensors and Real-Time Monitoring The Internet of Things (IoT) has introduced smart sensors that continuously monitor equipment and building conditions in real time. For example, a facility manager can deploy sensors in HVAC systems to track temperature, humidity, and airflow. These sensors send alerts if conditions deviate from preset parameters, allowing for immediate intervention before issues escalate. This proactive monitoring helps maintain air quality and comfort while reducing energy costs. | |
 | Predictive Analytics for Failure Prediction Predictive analytics uses historical data and machine learning algorithms to forecast when equipment may fail. In facilities management, this can be particularly useful for critical systems like elevators or chillers. By analyzing usage patterns and performance data, a facility manager can predict when maintenance is needed to prevent unexpected breakdowns. |
 | Automation of Maintenance Workflows Automation streamlines maintenance processes, reducing manual effort and minimizing human error. Facility management software can automate the scheduling and tracking of maintenance tasks. For instance, a commercial building might implement a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) that automatically generates work orders when IoT sensors detect that air filters in HVAC units need changing. This ensures timely maintenance, keeps systems running efficiently, and frees up facility managers to focus on strategic planning rather than administrative tasks. |
Conclusion:
The goal of predictive maintenance is to anticipate and foresee issues before they occur. This allows facility managers to implement preventative measures to avoid disruptions down the line. Embracing technological advancements can help facilities predict potential issues to not only enhance operational efficiency but also position facility managers to tackle the challenges of modern building management. As technology continues to evolve, the potential for preventative and predictive maintenance will expand, leading to smarter, more sustainable facilities.
Contact our team today to learn how we can help you implement preventative and predictive maintenance!




